Second harmonic Rayleigh scattering (HRS)
HRS is a non-linear optical process that can provide information on the structure of liquids at the molecular level.
Measuring the HRS signal of a solution involves focusing ultra-fast laser pulses onto a cell containing the sample. The output light produced by HRS is collected at right angle at a frequency twice that of the incident laser, with a cooled CCD detector.
Information about molecular structure and symmetry can be obtained through polarization-resolved HRS experiments.

(a) Spectrum of the HRS intensity at 400 nm of a 0.2M dAMP aqueous solution.
(b) Dependence of the HRS intensity from the 0.2M dAMP aqueous solution with the square of the fundamental average power.
C. Jonin et al. J. Chem. Phys. 159, 054303 (2023)
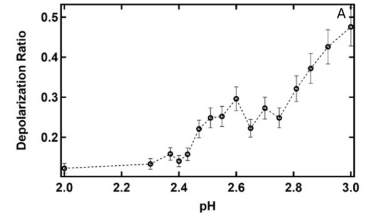

Depolarization ratio evolution as a function of pH for (A) atelocollagen and (B) telocollagen.
J.De Lizaraga et al. J. Physical Chem B, 2025